All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The gvhd Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the gvhd Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The gvhd and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The GvHD Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Medac and supported through grants from Sanofi and Therakos. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View GvHD content recommended for you
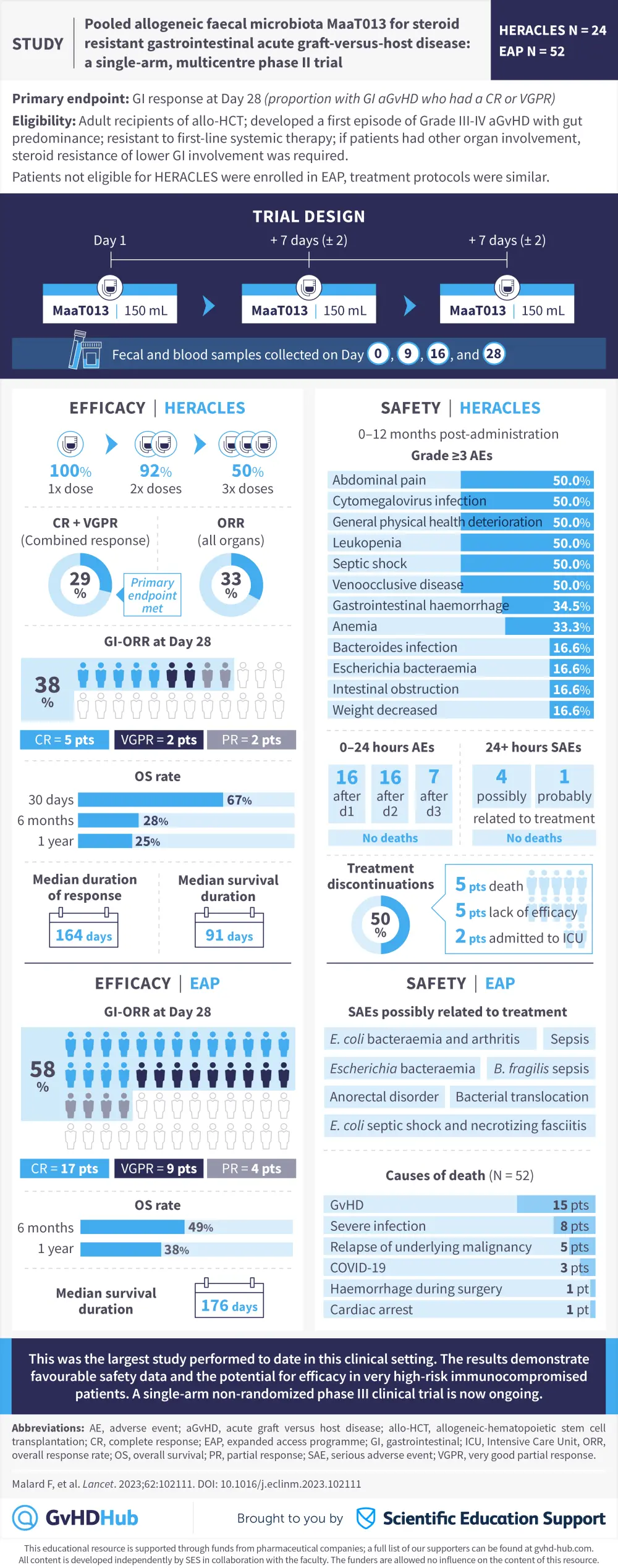
Visual abstract| Pooled allogeneic faecal microbiota therapy for steroid resistant GI-aGvHD
Do you know... The primary endpoint of the phase II HERACLES trial was GI response at Day 28 post-treatment administration. What was the overall GI-ORR for all patients in the HERACLES trial?
Severe gastrointestinal acute graft versus host disease (GI-aGvHD) is a serious complication that can occur after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT). Gut dysbiosis and a loss of bacterial diversity in the intestinal microbiome post-transplantation is thought to be an important factor in the development of the condition.
Fecal microbiota transplant is currently under investigation for the treatment of GI-aGvHD, with several pilot studies highlighting encouraging data. While the issue of donor sourcing remains a problem for fecal microbiota transplantation, one potential solution has been the development of a standardized fecal microbiota transplant product, MaaT013. This new form of microbiota therapy has previously been reported on the GvHD Hub.
Recently, Malard et al. performed the multicenter, single arm phase II HERACLES study (NCT03359980) investigating the safety and efficacy of MaaT013 in patients diagnosed with steroid-refractory GI-aGvHD. Here, we summarize the key results.
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content

