All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The gvhd Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the gvhd Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The gvhd and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The GvHD Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Medac and supported through grants from Sanofi and Therakos. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View GvHD content recommended for you
KD025 for chronic GvHD: an update
During the 46th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) two posters were presented by Madan Jagasia on KD025 (belumosudil). KD025 is an orally available Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase 2 (ROCK2) selective inhibitor, which down regulates proinflammatory T-helper 17 (Th17) cells and upregulates T-regulatory cells to reestablish immune homeostasis. The data presented were updates from two trials in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGvHD); the KD025-208 trial (NCT02841995), a phase IIa, dose escalation study that evaluated safety, tolerability, and activity of KD025 in adults,1 and the phase II ROCKstar study (KD025-213, NCT03640481), which examined efficacy and safety of KD025 in adults and adolescents after ≥ 2 prior lines of systemic therapy.2
Study design of KD025-2081
- Phase IIa, open label, dose escalation study that evaluated safety, tolerability, and activity of KD025 in patients aged ≥ 18 years with cGvHD after failing 1–3 prior lines of therapy.3
- Primary endpoint: Overall response rate (ORR) per 2014 National Institute of Health (NIH) criteria.
- Secondary endpoints: Duration of response (DOR), corticosteroid dose reduction, failure-free survival (FFS), and Lee Symptom Scale (LSS) score.
- 54 patients were enrolled into three dose cohorts:
- Cohort 1: 200 mg once daily (n = 17)
- Cohort 2: 200 mg twice daily (n = 16)
- Cohort 3: 400 mg once daily (n = 21)
- The median duration of follow-up was 29 months.
ROCKstar study design/patient characteristics2
- Phase II, randomized, multicenter trial to investigate the safety and efficacy of KD025 for the treatment of patients ≥ 12 years of age with cGvHD, after two to five prior lines of systemic therapy.
- Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive:
- Cohort 1: KD025 200 mg once daily (n = 66), or
- Cohort 2: KD025 200 mg twice daily (n = 66).
- Patients were stratified based on cGvHD severity, and prior ibrutinib/ruxolitinib treatment.
- Primary endpoint: ORR per 2014 NIH criteria.
- Secondary endpoints: Safety, DOR, corticosteroid dose reduction, FFS, LSS score, and overall survival.
- Patient characteristics were well balanced across the treatment arms.
- 132 patients participated, with a median age of 56 years, and a median of four prior lines of therapy. About half of the patients (52%) had four or more organs involved, and a third of patients (34%) had received prior ibrutinib. 72% of patients were refractory to prior line of therapy and two third (67%) of patients had severe cGvHD according to the NIH criteria.
Results1,2
Efficacy
- The median treatment duration in the intent-to-treat population for the KD025-208 trial was 8.4 months, while it was much shorter for the overall population of the ROCKstar trial, at 4.3 months.
- ORR was 65% (95% CI, 51–77%) across all cohorts for the KD025-208 trial, and ~73% in the ROCKstar trial. Responses were achieved across all key subgroups (Figure 1).
- Patients with non-severe GvHD had an ORR rate of 83% in the KD025-208 trial and 77% in the ROCKstar trial.
- Patients with greater than four organs involved had an ORR of 70% and 79% in the KD025-208 trial and the ROCKstar trial, respectively.
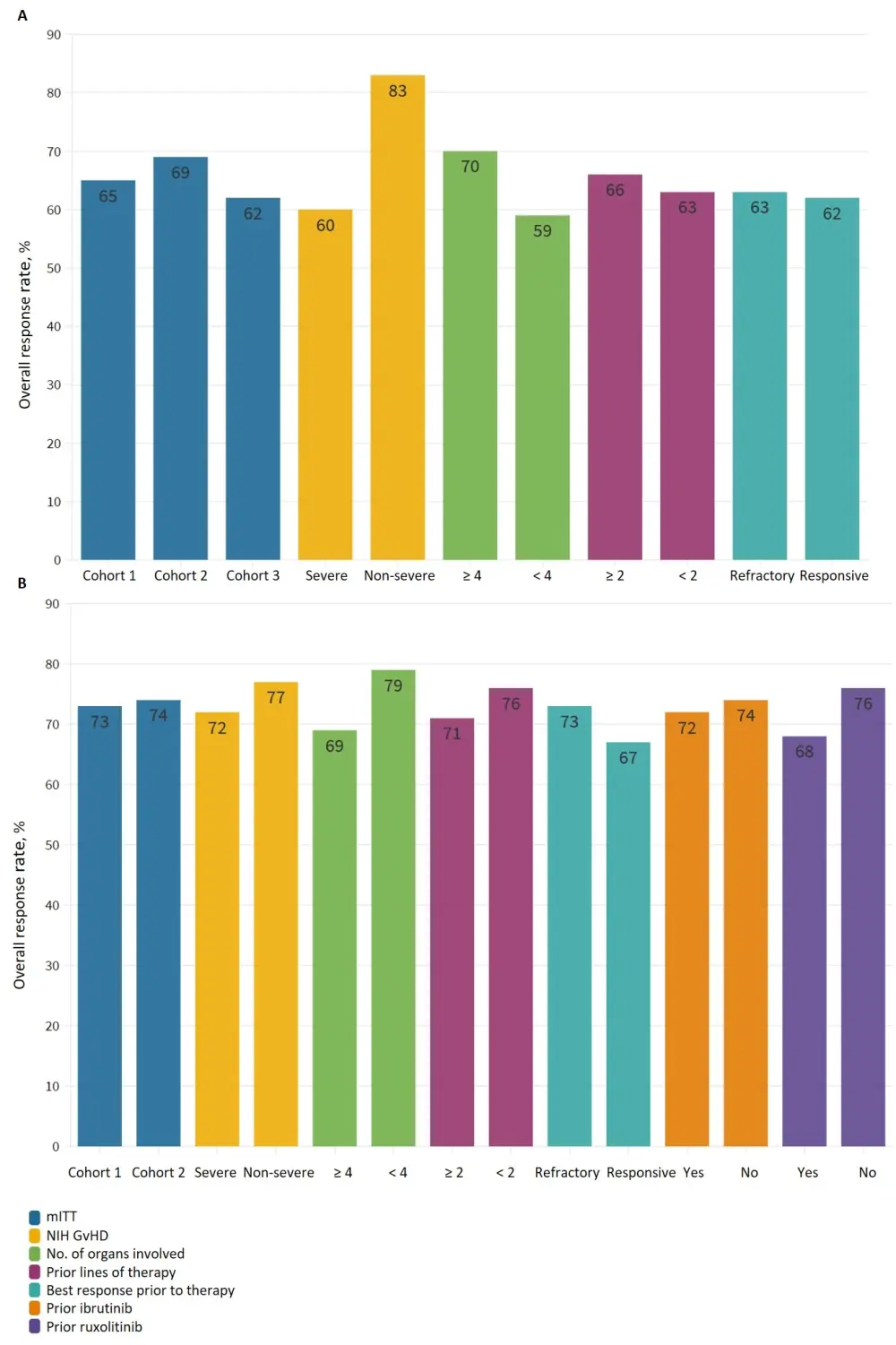
A KD025-208 trial. B ROCKstar trial.
GvHD, graft-versus-host disease; mITT, modified intent-to-treat; NIH, National Institute of health; ORR, overall response rate.
In the KD025-208 trial1:
- Complete response was seen in all affected organs except for the lung (partial responses only).
- 19% of patients completely discontinued corticosteroids.
- 50% of patients had a clinically meaningful improvement in LSS scores.
- FFS at 6, 12, and 24 months was 76%, 47%, and 33% respectively, with a median DOR of 35 weeks for all cohorts.
- 23% of patients remained on therapy > 1.5 years.
In the Rockstar trial2:
- Four patients achieved a complete response.
- DOR was not reached at the time of data cutoff and responses were maintained for ≥ 20 weeks in 49% of responders.
Safety
Safety results for both trials are summarized in Table 1.
- Four on-study deaths (7%) were reported in the KD025-208 trial, all from Cohort 3, and were considered unrelated to the drug.
- Causes of death were leukemia relapse, pneumonia of unknown pathogen, cardiac arrest, and GvHD progression.
- Five on-study deaths (4%) were reported in the ROCKstar trial, with four (hemothorax, aspiration pneumonia, acute myeloid leukemia relapse, and cardiac arrest) considered unrelated to the drug
- The death considered related to the drug was caused by severe nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting, leading to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.
- Drug related events occurred in approximately half of the patients across both trials, however, only few led to treatment discontinuation in the KD025-208 trial.
Table 1. Safety results1
|
Result |
KD025-208 trial |
ROCKstar trial |
|
AE, adverse event; ITT, intent-to-treat; SAE, secondary adverse event; N/A, not available. |
||
|
Median treatment duration, months |
8.4 |
4.3 |
|
Any-grade AE, % |
98 |
95 |
|
Grade 3/4 AE, % |
61 |
38 |
|
SAE |
43 |
28 |
|
Drug-related events |
|
|
|
Any AE |
54 |
50 |
|
SAE |
0 |
3 |
|
AE leading to discontinuation |
6 |
N/A |
|
On study deaths |
7 |
4 |
- Commonly reported adverse events (AEs) included upper respiratory tract infections, fatigue, and diarrhea which were the most frequently reported (Table 2).
Table 2. Commonly reported AEs1,2
|
AE |
KD025-208 |
ROCKstar |
||
|
Cohort 1 |
Cohort 2 |
Cohort 1 |
Cohort 2 |
|
|
AE, adverse event; ITT, intent-to-treat; N/A, not available. |
||||
|
All-grade AE in ≥ 20% of patients, % |
|
|
|
|
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
53 |
56 |
21 |
24 |
|
Diarrhea |
35 |
31 |
30 |
27 |
|
Fatigue |
35 |
19 |
39 |
24 |
|
Nausea |
35 |
25 |
26 |
26 |
|
Liver-related abnormalities |
47 |
38 |
18 |
24 |
|
Dyspnea |
18 |
38 |
30 |
17 |
|
Peripheral edema |
17 |
25 |
26 |
17 |
|
Cough |
6 |
25 |
29 |
20 |
|
Headache |
24 |
19 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Hypertension |
29 |
13 |
N/A |
N/A |
- In the KD025-208 trial, Grade ≥ 3 anemia, neutropenia or thrombocytopenia were seen in less than 10% of patients, while other more common severe adverse events were related to dyspnea (24%), GGT increase and hyperglycemia (13% each), and anemia and lung infections (11% each)
Conclusion
KD025 is well tolerated and demonstrates encouraging lasting responses leading to reduced corticosteroid use in adolescents and adults with cGvHD. Responses were seen across all subgroups including those with more than four organs involved, prior to ruxolitinib or ibrutinib use and more than four prior lines of therapies. There was no significant improvement in response with increased dose across both trials between the 200 mg once daily or twice daily groups. The most common side effects of KD025 included upper respiratory tract infection, liver related abnormalities, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea.
Based on an earlier analysis of the KD025-208 study, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted KD025 breakthrough therapy designation in heavily pretreated patients with R/R cGvHD. The ROCKstar study met its primary endpoint, however, the secondary endpoint data are not yet available.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
Which consideration most strongly guides your decision to escalate therapy in SR-aGvHD?

