All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The gvhd Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the gvhd Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The gvhd and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The GvHD Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Medac and supported through grants from Sanofi and Therakos. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View GvHD content recommended for you
The AGAVE-201 trial: Safety and efficacy of axatilimab at three different doses
Do you know... Which dose of axatilimab was seen as the most effective and had the least toxicity?
During the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition, Wolff presented results from the phase II AGAVE-201 (NCT04710576) trial of axatilimab, an investigational anti-colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor antibody, for the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGvHD).1 We summarize the key findings below.
The GvHD hub previously reported positive topline results from the AGAVE-201 trial, indicating the primary endpoint was achieved.
Study design1
In this study, 241 patients (≥2 years) with recurrent or refractory cGvHD, who had received two or more prior lines of therapy, were divided into three cohorts in which they received axatilimab, intravenously, at either 0.3 mg/kg every 2 weeks, 1 mg/kg every 2 weeks or 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks. Patients were permitted to use concomitant medications such as corticosteroids (65%), calcineurin inhibitors (28%), or mTOR inhibitors (12%) but were prohibited from receiving supplementary systemic cGvHD therapy.
The primary endpoint was the overall response rate at 24 weeks (6 cycles) as defined by the National Institute of Health (NIH) 2014 consensus criteria. The key efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients reporting a clinically significant reduction of symptoms, measured using the modified Lee Symptom Scale score. Safety endpoints included the frequency and severity of adverse events (AEs).
Efficacy outcomes1
The primary endpoint of overall response rate was met across all cohorts. Figure 1 illustrates efficacy endpoint data within each dose cohort.
Figure 1. Efficacy outcomes of axatilimab*
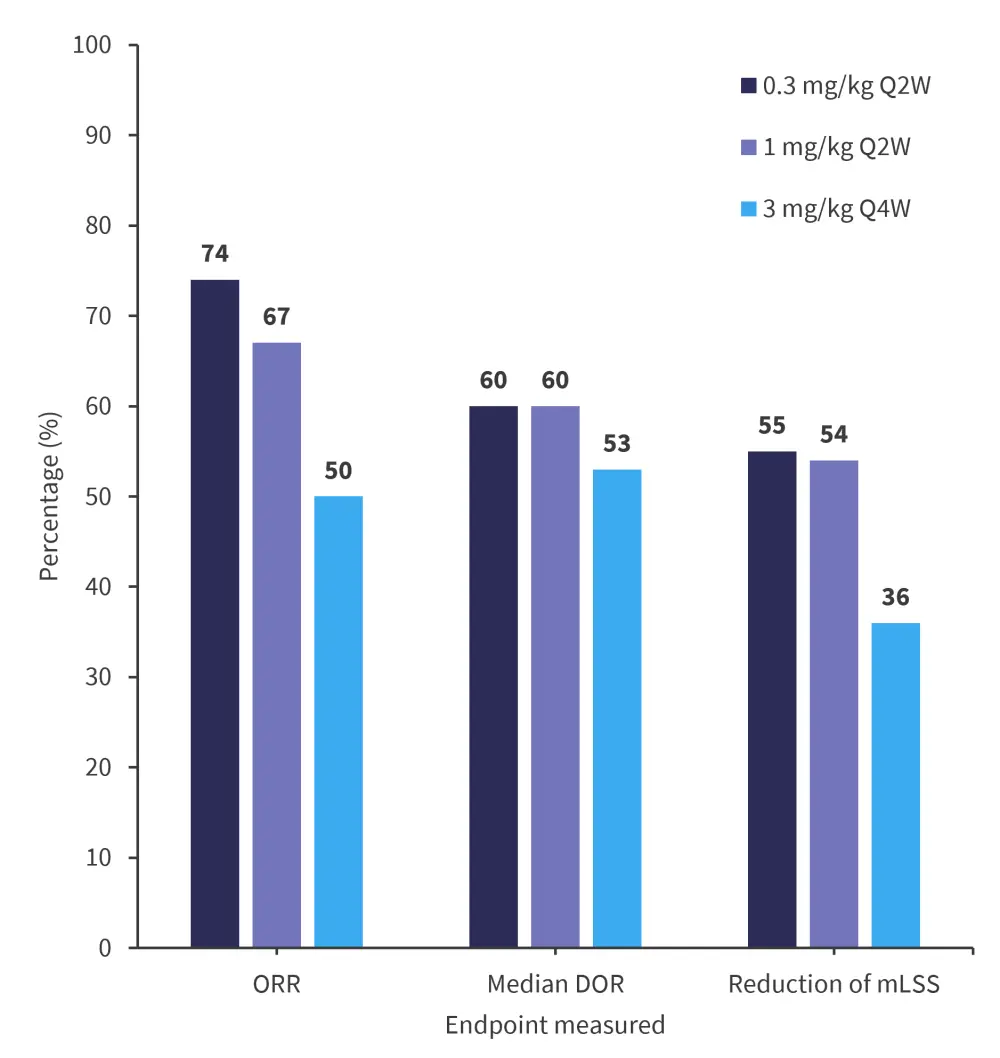
ORR, overall response rate; DOR, duration of response; mLSS, modified Lee Symptom Scale; Q2W, every 2 weeks; Q4W, every 4 weeks.
*Adapted from Wolff.1
Safety outcomes1
Three cytomegalovirus infections were reported in the higher-dose cohorts. Table 1 summarizes AEs that occurred in each cohort.
Table 1. Safety results of axatilimab*
|
Q2W, every 2 weeks; Q4W, every 4 weeks; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; TRAE, treatment-related adverse event. |
|||
|
|
0.3 mg/kg |
1 mg/kg |
3 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Drug discontinuation due to TEAEs |
6.3 |
22.2 |
17.7 |
|
Fatal AEs |
1.3 |
8.6 |
7.6 |
|
Most frequent Grade ≥3 TRAEs |
|||
|
Blood creatine phosphokinase increase |
0 |
7.4 |
15.2 |
|
Periorbital edema |
0 |
1.2 |
6.3 |
|
Pneumonia |
3.8 |
7.4 |
5.1 |
|
Gamma-glutamyl transferase increase |
0 |
1.2 |
5.1 |
Conclusion
Data presented from the AGAVE-201 study indicates that axatilimab, when administered at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg every 2 weeks, is an effective treatment option with a manageable safety profile for patients with recurrent or refractory cGvHD.1 A notable reduction in symptom burden was reported by most patients, with AEs being largely of low grade and reversible in most cases.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content


