All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The gvhd Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the gvhd Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The gvhd and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The GvHD Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Medac and supported through grants from Sanofi and Therakos. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View GvHD content recommended for you
Immunosuppressive efficacy and safety of MSCs bioengineered with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) in GvHD preclinical models
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are a promising therapy candidate for the treatment of graft-versus-host disease (GvHD). Although MSCs are well-tolerated in patients with GvHD, their insufficient immunosuppression at the sites of inflammation remains a challenge.1,2 To address this limitation, Sirpilla et al. introduced chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) technology to MSCs to enhance their immunosuppressive efficacy at inflammation sites.1,2
In GvHD, the host epithelial tissues are susceptible to donor immune cell attack through the interaction of T-cell integrins with E-cadherin (Ecad) expressed on epithelia. Thus, Sirpilla et al.1 hypothesized that an anti-Ecad CAR-MSC (EcCAR-MSC) with Ecad+ (human, mouse, and canine) cross-reactivity and a CD28ζ intracellular signaling domain would induce antigen-specific immunosuppression at these inflammatory target tissue sites.1,2 The possible mechanism of action of EcCAR-MSCs is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Mechanism of CAR-MSCs for the treatment of GvHD*
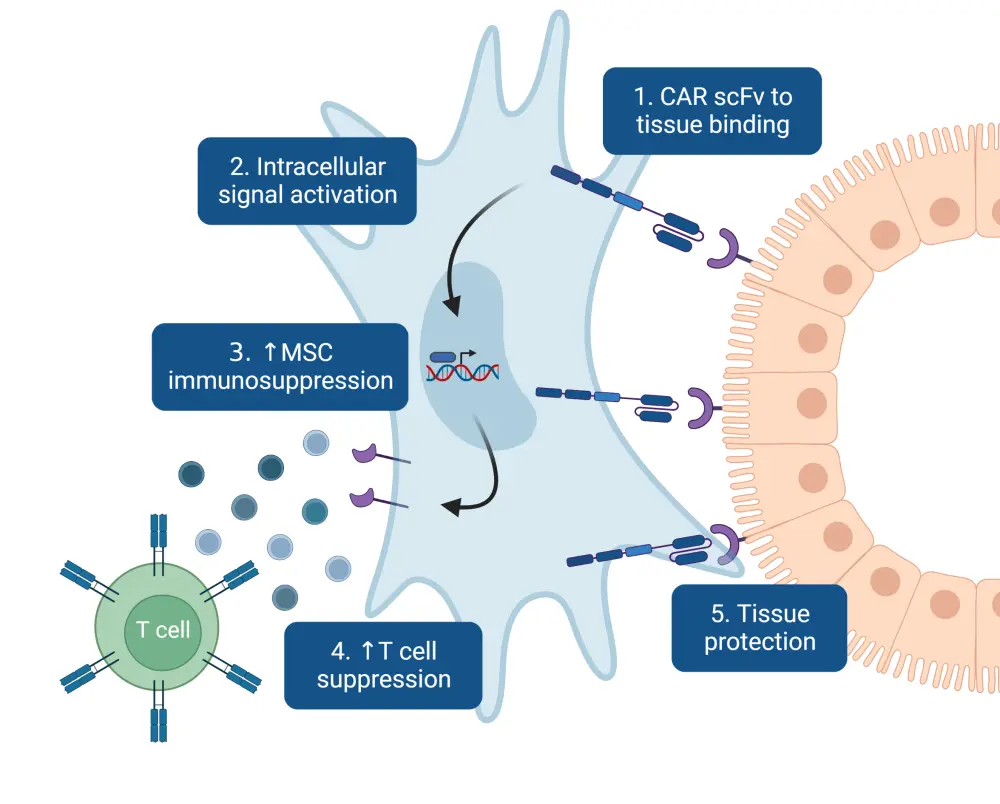
CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; GvHD, graft-versus-host disease; MSC, mesenchymal stromal cells; ScFv, single-chain variable fragment.
*Adapted from Sirpilla, et al.1 Created with BioRender.com
Here, we summarize the key findings of a study investigating immunosuppressive efficacy and safety of EcCAR-MSCs in GvHD preclinical models, presented was given at the 2023 Tandem Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings of ASTCT and CIBMTR.
Methods1,2
EcCAR-MSCs were developed by transducing CAR into adipose-derived MSCs via lentiviral vector enhancement. CD28 signal was selected for its ability to activate downstream immunosuppressive factors.
To test T-cell immunosuppression in vitro, MSCs were cocultured for 24 hours with activated donor T cells with or without antigen-specific Ecad stimulation.
The in vivo testing was done using GvHD xenograft models. GvHD was induced in NOD-SCID-γ-/- mice via intravenous injection of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mice were then treated with intraperitoneal injections of CAR-MSC, untransduced MSCs (UTD-MSC), or vehicle control to monitor weight loss, clinical GvHD score, human T cell suppression, and survival outcomes.
Mechanism of CAR-MSCs
- Mechanisms underlying superior immunosuppression in EcCAR-MSCs upon CAR stimulation were interrogated via RNA sequencing, serum cytokine assays, and immunophenotype analyses.
- To corroborate transcriptional enrichments, serum cytokines were analyzed.
Safety of CAR-MSCs
- The safety of EcCAR-MSCs was investigated in vivo by comparing clearance profiles with UTD-MSCs.
- Additionally, hematologic and organ toxicity studies were carried out in healthy canines through intraperitoneal EcCAR-MSC injection.
Results1,2
- Cocultures with antigen-stimulated CAR-MSCs led to significant T-cell suppression (p ≤ 0.01) compared with unstimulated CAR-MSCs or UTD-MSCs.
- In GvHD xenograft models, mice treated with CAR-MSCs exhibited significantly reduced weight loss, decreased clinical GvHD score (3 vs 5.2 score; p = 0.0014), increased T-cell suppression (60 vs 450 cells/uL; p = 0.0039), regulator T-cell induction (6.7 vs 2.1% in CD4+ cells), and improved overall survival compared with controls.
Mechanism of CAR-MSCs
- Functional CAR-MSCs were supported by mechanistic studies that revealed prominent immunosuppressive gene expression profiles.
- Mice treated with stimulated EcCAR-MSCs vs UTD-MSCs had elevated anti-inflammatory serum cytokines, such as interleukin-10, TNFα, and G-CSF. Immunophenotypic analyses revealed upregulated T-cell inhibitory receptor expression, including programmed death-1 and galectin-9, on stimulated EcCAR-MSCs vs UTD-MSCs (Figure 2).
- CD28-linked transcription factors such as NFκB and JUN were upregulated in Ecad-stimulated CAR-MSCs only.
Figure 2. Serum cytokine assays and immunophenotype analyses*
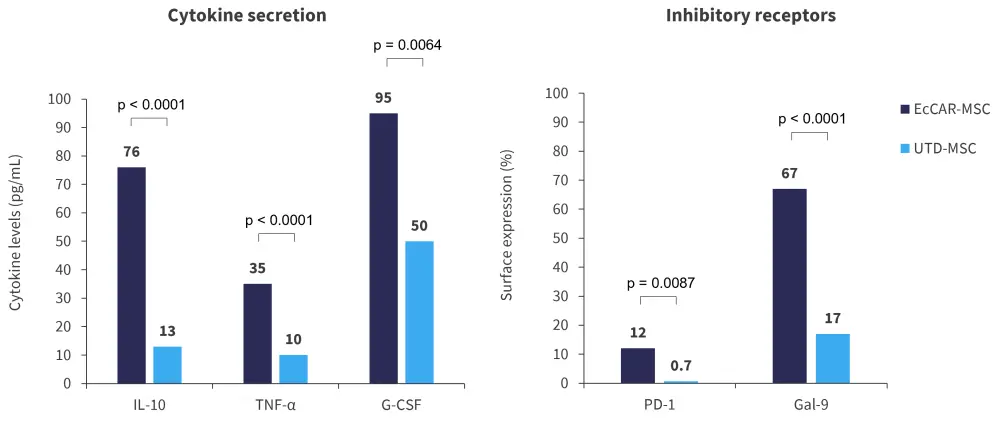
EcCAR-MSC, E-cadherin targeted chimeric antigen receptor–mesenchymal stromal cells; Gal, galectin; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; PD, programmed death; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; UTD-MSC, untransduced mesenchymal stromal cells.
*Adapted from Sirpilla, et al.1,2
Safety of CAR-MSCs
- Compared to UTD-MSC, CAR-MSCs showed similar stem and clearance profiles.
- CAR-MSCs were also well-tolerated in healthy canine models, showing no hematologic or organ toxicity following administration.
Conclusion1,2
The findings demonstrate EcCAR-MSCs as a novel therapeutic platform to enhance MSC antigen-specific immunosuppression in GvHD with no toxicity. EcCAR-MSCs will next be employed in a phase I clinical trial for patients with steroid-refractory acute GvHD, with alternative CAR-MSC designs also in progress for other autoimmune disease treatments.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content
Your opinion matters
Which consideration most strongly guides your decision to escalate therapy in SR-aGvHD?


